In the wake of unprecedented challenges faced by Vietnam Railways, the prime minister of Vietnam, Pham Minh Chinh, approved an ambitious railway development plan on October 19, 2021. The 2021-30 rail network strategy, with a vision up to 2050, envisages the construction of nine new lines across the country with an aggregate length of 2,632 km at a total investment of Vietnamese Dong (VND) 240 trillion or $10.3 billion. The development strategy also includes plans to upgrade seven existing railway lines.
Key features of the railway development plan
As per the rail network expansion strategy, the railways are expected to handle 11.8 million tonnes (mt) of freight, representing 0.27 per cent of the market and 460 million passengers with a market share of 4.4 per cent by the year 2030. Furthermore, urban passenger transport by railway is projected to meet approximately 15 per cent to 20 per cent of the demand for public passenger transport in Hanoi and Ho Chi Minh City. The period from 2020 to 2030 will focus on developing the railway infrastructure and investment in important new routes as a basic development for the vision to 2050.
To attain the intended market share, 16 major routes with a cumulative length of 4,802 km, including seven existing lines and nine new lines, will be developed. The development of the North-South high speed railway project will be integral as the project will have a significant socio-economic impact, boosting the growth of sectors such as mechanics and high technology. Two routes are proposed to be constructed in the North-South high speed railway, namely, Hanoi-Vinh and Nha Trang-Ho Chi Minh City. Four of the new railway lines will be linked to seaports. For instance, the Yen Vien-Pha Lai route will be connected with the Cai Lan seaport. Railway routes connecting major economic zones such as Dong Ngoc Hoi-Lac Dao-Bac Hong, Thu Thiem-Long Thanh, and Ho Chi Minh City-Can Tho will also be prioritised.
In the next 10 years, the existing railway route of Hanoi-Ho Chi Minh City with a length of about 1,726 km will be gradually modernised to achieve an average speed of 50 km per hour to 60 km per hour for cargo trains and 80 km per hour to 90 km per hour for passenger trains. Railway stations with high transport demand will be renovated to improve the quality of service. To establish safe corridors across the entire system, a network of frontage roads, isolation barriers, safety corridor barriers, and overpass bridges at intersections with high traffic volumes will be built. Funds worth VND 47.3 trillion or $2.05 billion have been proposed for these upgradation plans.
 Upgradation of railway links between Vietnam’s Lao Cai station and China’s Hekou North station on the Kunming-Haiphong route between Vietnam and China will help facilitate trade in the Kunming-Lao Cai-Hanoi-Haiphong economic corridor. The economic corridor is an important trade route and Vietnam’s gateway to the Association of Southeast Asian Nations countries and China.
Upgradation of railway links between Vietnam’s Lao Cai station and China’s Hekou North station on the Kunming-Haiphong route between Vietnam and China will help facilitate trade in the Kunming-Lao Cai-Hanoi-Haiphong economic corridor. The economic corridor is an important trade route and Vietnam’s gateway to the Association of Southeast Asian Nations countries and China.
Apart from allocation from the state budget, the Vietnamese government also intends to issue bonds to fund the development of railway infrastructure, especially urban railway systems. Efforts will be made to mobilise maximum capital from all domestic and foreign economic sectors via official development assistance funds and preferential capital of foreign governments. Investment in railway infrastructure will be encouraged through policy incentives, project bonds, joint ventures and public-private partnerships (PPPs).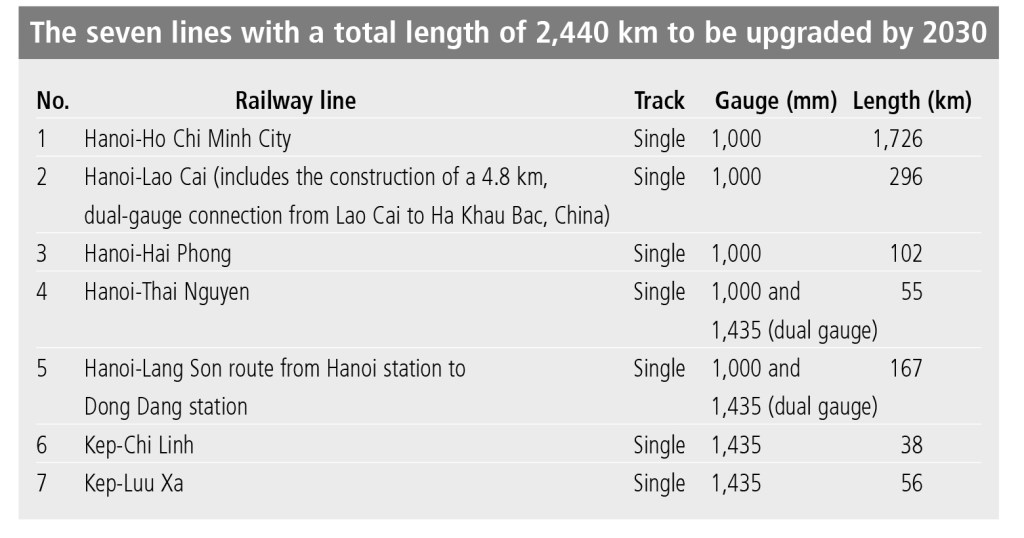
Future outlook
With the successful implementation of the expansion strategy by 2050, Vietnam will have a robust network of 25 railway routes with a length of 6,354 km. The crucial North-South express railway will be completed with Hanoi and Ho Chi Minh City becoming the main transit hubs. A new legislation on PPPs passed in 2020 is expected to boost investments in the infrastructure sector. Vietnam will also strengthen its ties with international partners, particularly those with advanced railway industries, while also incorporating Industry 4.0 technology in administering the railway system.

